On February 14th, a research team from Fudan University successfully overcame the core bottleneck of PEM electrolysis for hydrogen production by publishing an embedded carrier catalyst in the international authoritative journal Science. As a technology innovation enterprise incubated by Fudan University, Shanhai Hydrogen (Shanghai) New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. has fully promoted this heavyweight achievement to industrialization. Trina Green Hydrogen will leverage this new technology from strategic partners to jointly create a new generation of PEM electrolyzers, achieving significant cost reductions, improved product energy efficiency, and increased operating lifespan.

PPEM (proton exchange membrane) electrolysis technology is one of the most cutting-edge technologies currently available, with its small size, high current density, and high flexibility, which has attracted much market attention. However, PEM technology relies on oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalysts, and currently, iridium and its oxides (IrO ₓ) are the only catalysts that can work stably in highly acidic PEM environments. As a precious metal, iridium is expensive and has extremely limited reserves in the Earth's crust, which poses a huge economic obstacle to the large-scale deployment of PEMWE electrolysis water systems. Therefore, developing a low-cost, efficient, and stable OER catalyst has become an urgent core issue that the global academic and industrial communities need to address.
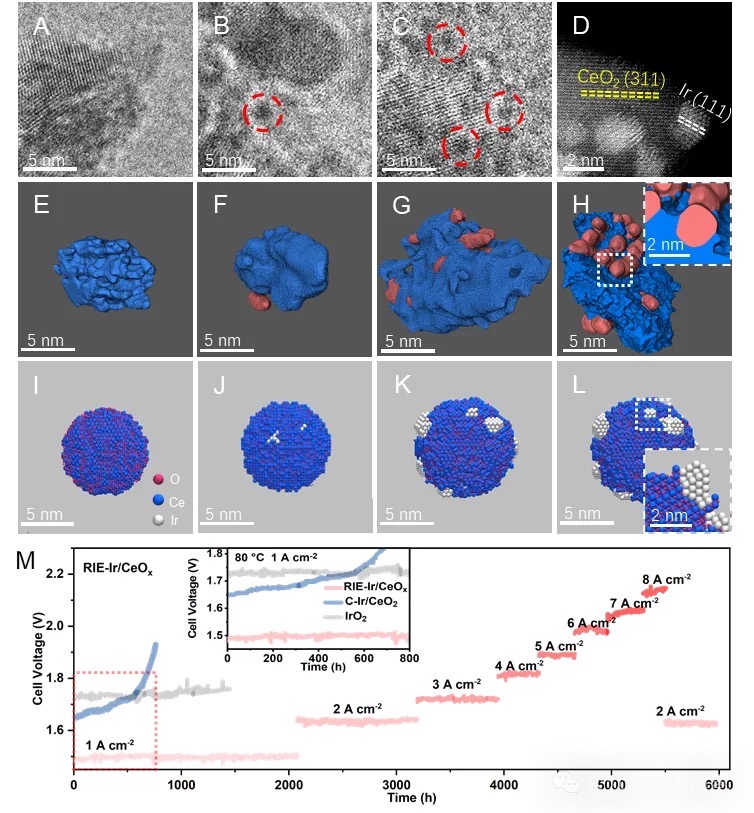
This time, an innovative catalyst design scheme is released, which embeds iridium oxide nanoparticles into cerium oxide support to form a stable and efficient supported catalyst, achieving a comprehensive technological breakthrough from cost to energy efficiency. The three major breakthroughs of Professor Zhang Bo's team at Fudan University have given a boost to the development of the hydrogen energy industry.
Breakthrough ① Cost reduction of 85%: Embedded catalysts reduce the amount of precious metal iridium by 85%, resulting in a significant decrease in costs;
Breakthrough 2: Energy efficiency jumps by 65%: catalyst activity has been improved to the international top level, and the efficiency of water electrolysis far exceeds existing technologies;
Breakthrough ③ with a lifespan of up to 15 years: Accelerated aging test for 6000 hours without performance degradation, equipment lifespan extended by 50%, and globally leading stability.
This achievement marks the first time internationally that China has achieved and surpassed all the targets set by the US Department of Energy for PEM electrolyzed water catalysts by 2026, marking a leap from "following" to "leading" in the green hydrogen race.

Trina Green Hydrogen and Shanhai Hydrogen signed a strategic cooperation agreement in December 2024, jointly tackling many existing technical challenges in the hydrogen energy field. Through efforts in technology research and development, product innovation, market expansion, and other aspects, they promote the coupling application of ALK and PEM electrolysis cell systems, and work together to create a more complete and efficient hydrogen energy industry chain ecosystem.
In the future, Trina Green Hydrogen will leverage the technological achievements of this innovative catalyst to jointly create a cost-effective PEM electrolysis cell, accelerating the development of the green hydrogen industry. Collaborating with an internationally leading innovative technology team, we believe that Trina Green Hydrogen's new generation PEM electrolyzer will have a broader market space.




